Air Curtain vs. Open Burning: Emissions Comparison
Disposing of wood and vegetative waste is a challenge faced by land-clearing contractors, municipalities, and forestry agencies worldwide. Traditionally, the simplest method has been open burning—piling debris and setting it alight. However, as environmental regulations tighten and sustainability becomes a priority, air curtain burners are emerging as the cleaner, more efficient alternative.
Below, we break down how air curtain burning compares to open burning—especially when it comes to emissions, environmental impact, and real-world performance.
Key Takeaways
- Air Curtain Burners reduce smoke by ~97% compared to open burning, operating well under 10% opacity while open burning often reaches 80–100%.
- Cleaner combustion = fewer particulates, less black carbon, and lower impact on local air quality for communities, operators, and job sites.
- Open burning is inefficient and produces high levels of PM, CO, VOCs, and methane—many of which are harmful air pollutants.
- Air Curtain Burners control the burn, forcing smoke particles back into the hot zone where they re-burn, creating a much cleaner emission profile.
- On-site waste elimination reduces trucking emissions, which often outweigh the small amount of diesel used to run the fan.
- Most states allow air curtain burners in places where open burning is restricted, and many agencies recommend or prefer them for land-clearing and storm debris.
- Operating costs are low, since the wood waste fuels itself once ignited, and the same crew can often run multiple machines at once.
- Air Burners systems are widely trusted by forestry agencies, municipalities, and contractors because they provide fast, compliant, environmentally responsible waste disposal.
What Is Open Burning and Why Is It a Problem?
Open burning is the uncontrolled burning of wood, brush, or vegetation in open air. Even though the method is inexpensive, it results in extremely inefficient combustion.
Because airflow is not regulated, oxygen levels fluctuate, causing incomplete burns. This leads to high levels of:
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
- Particulate matter (PM) and soot
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
- Methane (CH₄) and black carbon
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), open burning of vegetative waste contributes significantly to air pollution and is a regulated activity in most states. (See the EPA’s open burning guidance: https://www.epa.gov/openburning)
What Is an Air Curtain Burner?
An air curtain burner is an engineered combustion device that uses a high-velocity “curtain” of air to control the burn and significantly reduce smoke and emissions.
Unlike open burning, this is an enclosed firebox where air is forced across the top of the fire. This air curtain traps smoke particles, pushing them back into the combustion zone to reburn—resulting in a more complete and cleaner burn.
You can learn more about this technology on the official Air Burners product pages:
How Do Emissions Compare?
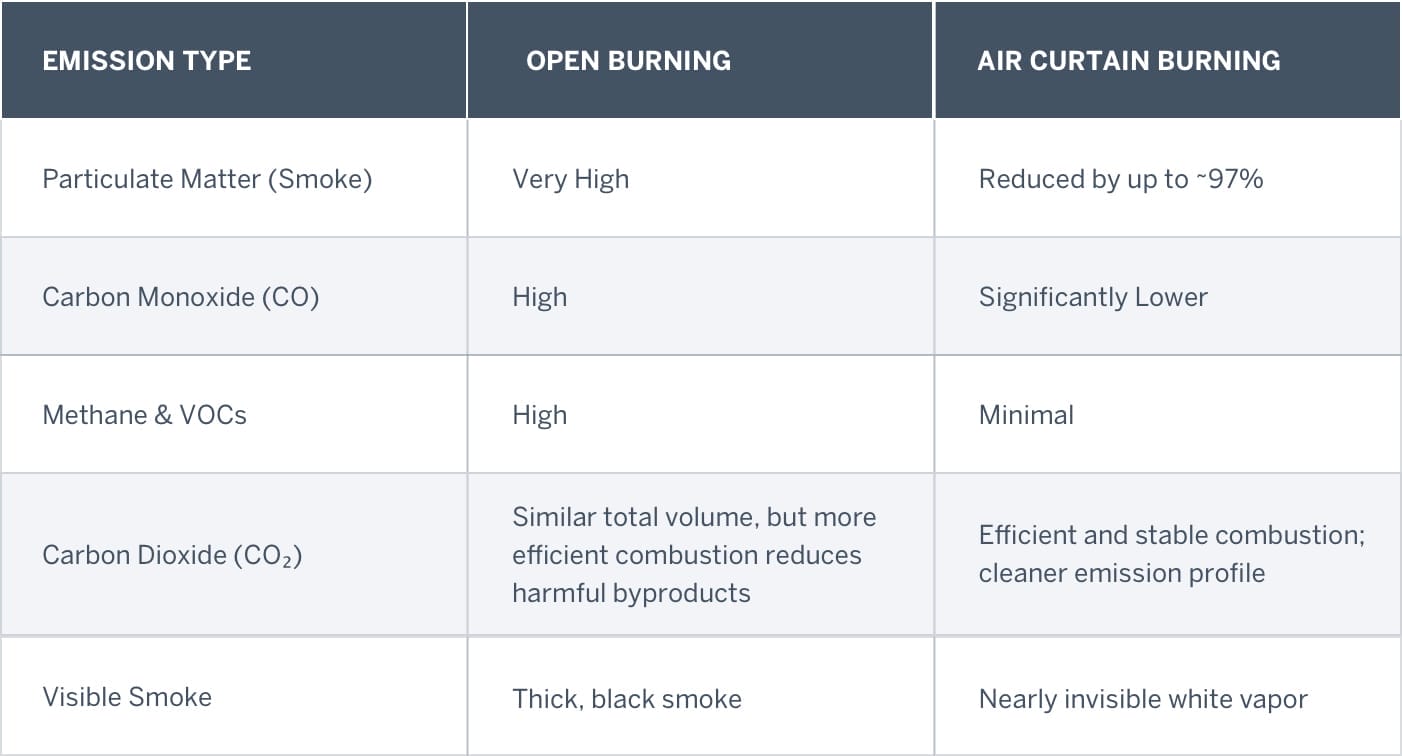
In simple terms: air curtain burners don’t eliminate emissions entirely, but they dramatically reduce harmful particulates and visible smoke. This makes them the preferred method under EPA guidelines for clean biomass disposal.
Why Are Air Curtain Burners Better for the Environment?
Air curtain burners offer a far cleaner and more environmentally responsible alternative to open burning because they create a controlled combustion zone that reburns smoke and particulates before they escape. This results in significantly fewer harmful emissions and dramatically reduced visible smoke, improving air quality for both operators and nearby communities.
Another major environmental advantage is on-site waste elimination. Because debris is processed where it’s generated, Air Burners systems reduce or eliminate the need for truck hauling, long transport routes, and the associated fuel use and emissions. In most real-world applications, the emissions avoided by not hauling debris far outweigh the small amount of fuel used to power the air curtain’s fan.
Although the system may use a small diesel engine to operate the fan, the fire itself is fueled by the biomass—not fossil fuel—making the entire process more efficient and far less polluting than traditional disposal methods. The result is a cleaner, lower-emission, and more sustainable solution for managing wood and vegetative waste.
Do Air Curtain Burners Meet EPA Standards?
Yes. Air Burners equipment has been tested for environmental performance expectations set by the U.S. EPA, the USDA Forest Service, and many state-level Departments of Environmental Protection. Because air curtain burners dramatically reduce particulate emissions compared to open burning, many states recommend or even require their use for land-clearing and storm-debris operations. The EPA does not publish a standalone “air curtain burner rule,” but their guidance on open burning—especially of vegetative waste—highlights the air-quality concerns that air curtain systems are specifically engineered to address.
Reference: EPA Open Burning Guidance https://www.epa.gov/openburning
Can Air Curtain Burners Be Used Anywhere Open Burning Is Restricted?
In many cases, yes. Even in regions where traditional open burning is restricted or prohibited, air curtain burners are often allowed because they significantly reduce smoke, particulate matter, and visible emissions. That’s why you’ll find Air Burners systems in use across:
- Federal and state forestry services
- Municipal landfills and disaster recovery operations
- Private contractors managing construction debris
Regulations differ from one county or state to the next, so it’s always best to check locally. Your county Fire Marshal normally can confirm what’s required in your area.
- In Florida and Georgia, mobile Air Burners are generally authorized through the state forestry departments.
- Stationary units may require an air-quality permit through the state environmental agency (such as Georgia EPD).
If you’re unsure where to start, your local Fire Marshal is the quickest path to a clear answer.
How Do Air Curtain Burners Work?
- Load the Waste: Clean wood and vegetative debris are placed into the FireBox.
- Ignition: A small amount of diesel is used to ignite the first pile—just like starting a campfire.
- Air Curtain Activated: A high-velocity fan creates an “air curtain” across the top of the FireBox.
- Combustion Cycle: Once the fire is established, it burns naturally with no additional fuel. The air curtain traps smoke and particulates, forcing them back into the hot zone where they re-burn.
- Ash Removal: What remains is a small amount of inert ash or biochar—typically 3–5% of the original waste volume (more if biochar is intentionally produced).
Air Burners’ patented systems, such as the FireBox, are engineered for high efficiency, low emissions, and minimal maintenance.
What About Portable or Mobile Options?
For contractors or disaster-response teams, mobility is key. All Air Burners systems are designed to be relocatable or portable and can be deployed directly to the work site.
For municipalities and energy projects, the PGFireBox and BioCharger convert biomass into clean, renewable electricity — combining waste disposal and power generation in one system.
How Much Cleaner Is Using Air Burners?
Using Air Burners is dramatically cleaner than traditional open burning. According to field tests and technical evaluations documented by Air Burners:
- Open burning typically produces 80–100% opacity smoke.
- Air Curtain Burners operate well under 10% opacity when used properly.
That’s a 90% reduction in visible smoke—a cleaner burn by an order of magnitude. The reason is simple: the air curtain holds smoke particles in the hottest zone of the FireBox, forcing them to re-burn instead of escaping into the air. This breaks down particulate matter, reduces black carbon, and eliminates the long-lasting smoldering that open piles are known for. The result: far less smoke, cleaner air, improved visibility, and a safer work environment for operators and surrounding communities.
FAQ: Common Questions About Air Curtain Burners
Q1: Are air curtain burners expensive to operate?
No. Air curtain burners are very low-cost to run. They only require a small amount of diesel for startup, and once the fire is established, the wood waste fuels itself—not external fuel. Daily operating costs are mainly labor, loader time, and basic maintenance.
For larger jobs, running multiple machines side by side reduces your cost per ton even further, because the same operator and loader can feed several units at once. That means higher throughput, lower labor cost per unit, and faster site cleanup.
Q2: Can I rent an air curtain burner?
Yes. Air Burners offers air curtain burners for rent through authorized dealers across the U.S. Visit Air Curtain Burners for Rent to find rental partners near you.
Q3: What kind of waste can I burn?
Air Curtain Burners are designed for clean, untreated wood waste and natural vegetative debris. This includes:
- Brush, limbs, and tree trimmings
- Logs and stumps
- Pallets and dimensional lumber as long as it’s untreated
- Storm debris and land-clearing waste
Q4: How long does one load burn?
Burn time depends on the type of wood waste and its moisture content, but air curtain burners are designed for continuous, all-day operation. Once the fire is established, new material is added at the same rate it burns. Most users run their units steadily throughout the workday, then allow the fire to burn down overnight. Ash or biochar is typically removed the next morning, leaving the FireBox ready for the next cycle.
Q5: Does it require special training?
While you don’t need a special trade license to run Air Burners, operator training is strongly recommended.
Air Burners offers a complete operator training and certification program (plus a webinar option) for all models offered. Training is provided by Air Burners field technicians and includes:
- Classroom instruction on safe, efficient operation and environmental best practices
- Hands-on training in the field using the customer’s own machine
- A certificate issued upon successful completion
A typical on-site course is a well-structured, two-day session at the customer’s location (in the U.S., Canada, and many overseas sites), focused on helping operators run the equipment efficiently, cleanly, and safely.
Cleaner, Safer, Smarter
Comparing air curtain vs open burning, the evidence is clear — air curtain technology provides a cleaner, more sustainable way to dispose of biomass. It minimizes air pollution, supports environmental goals, and reduces operational costs for agencies and contractors.
If your operation still relies on open burning, it’s time to consider upgrading to an Air Burners system — the proven solution trusted by governments, contractors, and forestry professionals worldwide.
Explore available systems here: Air Burners Product Line
And for official environmental data on burning emissions, visit: EPA: Open Burning and Air Quality
